
Deleting a swap file is an important step in managing your computer’s memory and optimizing its performance. A swap file, also known as a paging file, is a space on your hard drive that is used as virtual memory when your computer’s physical memory is running low. While swap files can be beneficial, they can also take up valuable disk space. In this step-by-step guide, we will show you how to delete a swap file and regain that space on your hard drive.
Step 1: Identify the Swap File
The first step in deleting a swap file is to identify its location on your computer. On most operating systems, the swap file is located in the root directory of your hard drive. It is often named “swapfile.sys” or “pagefile.sys”. If you are unsure of the location or name of your swap file, you can use the search function on your computer to find it.
Step 2: Disable the Swap File
Before you can delete the swap file, you need to disable it. This will prevent your computer from using the swap file while you are in the process of deleting it. To disable the swap file, go to your computer’s settings or control panel and navigate to the virtual memory settings. Here, you can adjust the size of the swap file or disable it completely. Select the option to disable the swap file and save your changes.
Step 3: Delete the Swap File
Once the swap file is disabled, you can proceed with deleting it. Open your file explorer and navigate to the location of the swap file. Right-click on the swap file and select “Delete” from the menu. You may be prompted to confirm the deletion, so make sure to double-check that you are deleting the correct file. After confirming the deletion, the swap file will be permanently removed from your hard drive.
By following these simple steps, you can easily delete a swap file and free up valuable disk space on your computer. Remember to always double-check the file you are deleting to avoid accidentally deleting important system files. Regularly deleting unnecessary swap files can help improve your computer’s performance and keep your hard drive running smoothly.
What is a Swap File?
A swap file, also known as a paging file or virtual memory file, is a file on your computer’s hard drive that is used to supplement the physical memory (RAM) when it becomes full. When your computer runs out of available RAM, it moves inactive data from the RAM to the swap file, freeing up space in the RAM for active processes.
The swap file is an essential component of the operating system, as it allows your computer to continue running smoothly even when it is low on physical memory. Without a swap file, your computer may become slow or unresponsive when it runs out of RAM.
By default, the swap file is automatically created and managed by the operating system. However, there may be situations where you want to delete the swap file manually, such as when you need to free up disk space or troubleshoot performance issues.
It is important to note that deleting the swap file can have consequences on your computer’s performance, as it may lead to increased reliance on physical memory and potential slowdowns. Therefore, it is recommended to only delete the swap file if you have a specific reason to do so and understand the potential impact.
Definition of Swap File
A swap file, also known as a paging file or virtual memory file, is a file on a computer’s hard drive that is used to supplement the physical RAM (random access memory) when it becomes full. When the RAM is insufficient to hold all the data that the computer needs to process, the operating system moves some of the less frequently used data from the RAM to the swap file.
The swap file allows the computer to continue running smoothly by providing additional memory space for the operating system to use. It acts as a temporary storage area for data that is not currently being actively used, but may be needed again in the future.
When the computer needs to access data that has been moved to the swap file, it retrieves it from the file and moves it back into the RAM. This process is known as swapping or paging. The swap file is typically located on the computer’s main hard drive, but it can also be stored on a separate drive or partition.
Knowing how to manage the swap file is important for optimizing system performance. By adjusting the size of the swap file or disabling it altogether, users can customize their computer’s memory usage to better suit their needs.
How Swap File Works
A swap file, also known as a paging file, is a file on your computer’s hard drive that is used as virtual memory. When your computer’s physical memory (RAM) is full, the operating system moves some of the data from RAM to the swap file to make room for new data.
The swap file acts as an extension of your computer’s RAM, allowing it to temporarily store data that is not currently being used. This can be useful when you have multiple programs running simultaneously and your computer’s RAM is being heavily utilized.
When you delete a swap file, you are essentially removing this virtual memory space from your computer’s hard drive. This can be done to free up disk space or to troubleshoot issues related to the swap file.
It’s important to note that deleting a swap file can have an impact on your computer’s performance, especially if you have limited RAM. If your computer frequently runs out of physical memory and relies heavily on the swap file, deleting it may cause your computer to slow down or crash.
If you decide to delete a swap file, it’s recommended to have enough physical memory (RAM) to handle your computer’s workload without relying heavily on virtual memory. Additionally, make sure to follow proper procedures and consult documentation specific to your operating system to avoid any potential issues.
Why Delete Swap File?
The swap file is a crucial component of the operating system that helps manage memory usage. It is used as a virtual memory extension when the physical memory (RAM) is full. However, there are several reasons why you might want to delete the swap file:
1. Privacy and Security: The swap file can contain sensitive information, such as passwords or encryption keys, that may be stored temporarily in the RAM. Deleting the swap file ensures that this data is not accessible to unauthorized users.
2. Performance Optimization: If your system has sufficient physical memory, the swap file may not be necessary. Deleting it can free up disk space and potentially improve overall system performance.
3. Troubleshooting: In some cases, a corrupted or misconfigured swap file can cause system instability or crashes. Deleting the swap file and recreating it can help resolve these issues.
4. Changing System Configuration: When making significant changes to your system, such as upgrading RAM or adjusting swap file settings, deleting the existing swap file may be necessary to ensure the changes take effect properly.
5. System Cleanup: Deleting the swap file as part of routine system maintenance can help keep your system clean and optimized.
Knowing how to delete the swap file is essential for managing your system’s resources effectively and ensuring optimal performance and security.
Reasons to Delete Swap File
The swap file is a crucial component of the operating system that helps manage memory usage. However, there are certain situations where you may want to delete the swap file:
1. Free up disk space: The swap file can take up a significant amount of disk space, especially if your system has limited storage capacity. By deleting the swap file, you can reclaim this space and use it for other purposes.
2. Improve performance: In some cases, the swap file may become fragmented or corrupted, leading to decreased system performance. Deleting the swap file and creating a new one can help resolve these issues and improve overall system performance.
3. Troubleshoot system errors: If you are experiencing frequent system crashes or errors, deleting the swap file can be a troubleshooting step. Sometimes, a corrupted swap file can cause these issues, and deleting it can help identify if the swap file is the root cause.
4. Change swap file configuration: If you want to change the size or location of the swap file, you will need to delete the existing swap file first. This allows you to configure the swap file according to your specific requirements.
5. Security concerns: In certain scenarios, such as when disposing of a computer or transferring ownership, you may want to delete the swap file to ensure that sensitive data stored in the swap file is not accessible to unauthorized individuals.
Overall, deleting the swap file can be beneficial in various situations, including freeing up disk space, improving performance, troubleshooting system errors, changing configuration, and addressing security concerns.
Benefits of Deleting Swap File
Deleting the swap file can provide several benefits to your system. Here are some of the key advantages:
| Improved Performance | By deleting the swap file, you can free up valuable disk space and improve the overall performance of your system. This is especially important if you have limited storage capacity. |
| Increased Security | Swap files can sometimes contain sensitive information, such as passwords or encryption keys. By deleting the swap file, you can ensure that this data is not accessible to unauthorized users. |
| Reduced Wear on SSDs | If you are using a solid-state drive (SSD), deleting the swap file can help reduce the wear on the drive. SSDs have a limited lifespan, and excessive read and write operations, such as those performed by the swap file, can shorten their lifespan. |
| Improved Stability | In some cases, a corrupted or bloated swap file can cause system instability or crashes. By deleting the swap file, you can resolve these issues and improve the overall stability of your system. |
Overall, deleting the swap file can have numerous benefits for your system, including improved performance, increased security, reduced wear on SSDs, and improved stability. If you are unsure how to delete the swap file, refer to the guide on how to delete swap file for step-by-step instructions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Delete Swap File
If you are wondering how to delete a swap file, this step-by-step guide will walk you through the process. A swap file is a space on your computer’s hard drive that is used as virtual memory when your RAM is full. Deleting the swap file can help free up disk space and improve system performance.
Step 1: Open a terminal window on your computer. You can usually find the terminal application in the “Utilities” or “Accessories” folder.
Step 2: Type the following command to view the current swap file:
sudo swapon --show
This command will display information about the active swap file, including its size and location.
Step 3: To disable the swap file, type the following command:
sudo swapoff -a
This command will turn off the swap file, allowing you to delete it.
Step 4: Use the following command to delete the swap file:
sudo rm /path/to/swapfile
Replace “/path/to/swapfile” with the actual path to your swap file. If you are not sure where the swap file is located, you can use the “find” command to search for it.
Step 5: Finally, you can verify that the swap file has been deleted by typing the following command:
sudo swapon --show
If the command does not display any output, it means that the swap file has been successfully deleted.
By following these steps, you can easily delete the swap file on your computer. Remember to exercise caution when deleting system files, as it can affect the stability and performance of your system.
Step 1: Identify Swap File Location
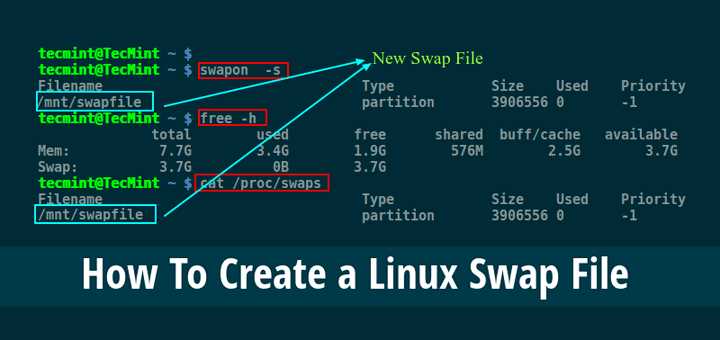
Before you can delete your swap file, you need to first identify its location on your system. The swap file is a special file that is used by the operating system to temporarily store data when your computer’s physical memory is full.
To find the location of your swap file, you can use the following command in the terminal:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
swapon --show |
This command displays the active swap devices and their locations. |
After running the command, you will see a list of swap devices along with their locations. Look for the swap file that you want to delete and take note of its location.
Once you have identified the location of your swap file, you can proceed to the next step to delete it.
Step 2: Disable Swap File
To delete the swap file, you first need to disable it. Follow the steps below to disable the swap file:
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Type the command
sudo swapoff -aand press Enter. This command will disable all swap files. - If you have multiple swap files and want to disable a specific one, use the command
sudo swapoff /path/to/swapfile, replacing/path/to/swapfilewith the actual path to the swap file you want to disable. - Verify that the swap file has been disabled by running the command
free -h. The output should show 0 bytes of swap memory.
Once you have disabled the swap file, you can proceed to the next step to delete it.

